Explore the top EDI software for logistics providers. Compare platforms that can automate key processes, boost accuracy, and improve customer satisfaction.
Third-party logistics (3PL) providers face many data challenges across the supply chain. Every new client brings unique requirements, from handling electronic data interchange (EDI) documents to coordinating shipments across warehouse and freight systems. Without the right technology, these processes often rely on manual data entry that slows onboarding and increases the risk of errors.
Modern EDI for 3PL gives logistics organizations the ability to automate order processing and gain real-time visibility into inventory and shipment status across the entire supply chain. The right solution can help providers reduce operational costs just by increasing the efficiency of data exchange, while also improving accuracy and customer satisfaction.
This guide explores the best EDI platforms for logistics operations today. Each solution has been evaluated for its ability to give 3PLs the tools they need to streamline operations and compete in a dynamic, fast-moving industry.
What Makes a Good EDI Solution for 3PLs and Logistics Providers?
Selecting the right EDI platform can make a measurable difference in how 3PLs manage their logistics operations. The best solutions address common pain points while also creating room to scale.
When evaluating EDI for logistics, organizations should look for solutions that deliver:
Fast and flexible EDI onboarding that reduces the time it takes to connect with new supply chain partners.
Logistics-specific documents, such as the warehouse shipping order and warehouse shipping advice.
WMS, TMS, and ERP integration to ensure data flows smoothly between business systems.
Real-time data exchange and visibility that keep operations aligned and improve decision-making.
API support alongside legacy systems so trading partners of all sizes can connect.
Transparent pricing models that support predictable scaling without surprise costs.
Top Platforms for EDI in Logistics
The logistics industry has no shortage of EDI systems, from long-standing providers that rely on legacy processes to modern, cloud-based solutions designed for speed and scalability. The right choice often depends on your trading partners, existing systems, and how quickly your business wants to onboard new customers.
These EDI systems represent some of the best EDI providers for logistics organizations, offering a range of approaches to help logistics companies get the most out of their operations. Data is taken from G2.
1. Orderful
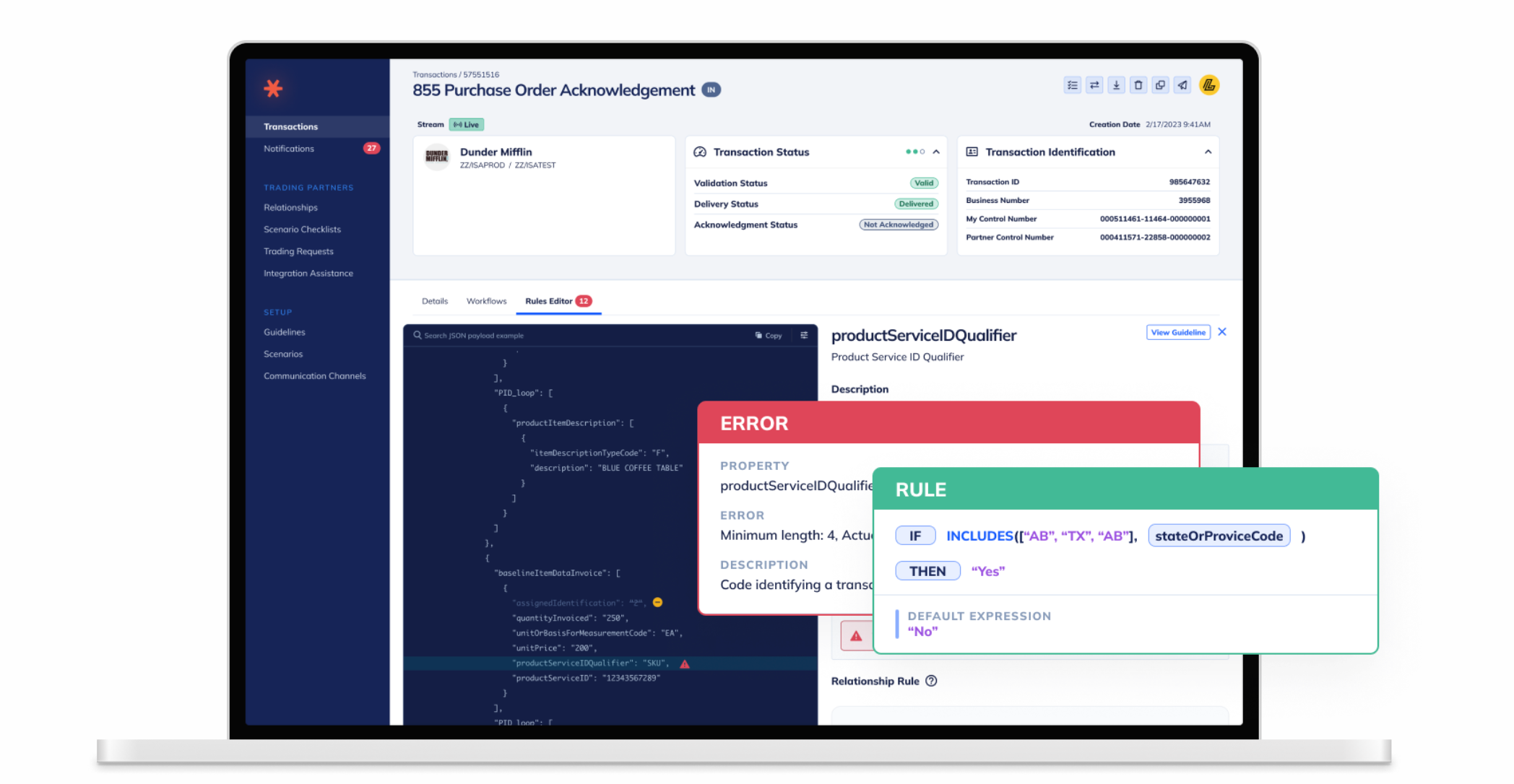
Orderful is a modern, API-first electronic data interchange platform built for 3PLs and logistics providers that need fast, flexible connections.
Benefits:
Fast partner onboarding with self-serve tools that reduce manual processes.
Logistics-specific support for logistics business documents, such as warehouse inventory adjustment advice.
Flat pricing with no per-document fees, making costs predictable as you scale.
Possible Drawbacks:
This platform is newer in the market compared to long-standing legacy providers.
Partners with older EDI systems may require training to get them up to speed with a new way of doing things.
The feature set is streamlined, which could feel limiting for enterprises that prefer highly customized workflows.
Businesses adopting Orderful benefit from modern integrations with warehouse management systems (WMS), transportation management systems (TMS), and enterprise resource planning (ERP) platforms, along with the scalability to support a growing network of trading partners.
2. SPS Commerce
SPS Commerce is one of the largest EDI providers in the logistics industry, with a long history of serving retail-focused supply chains. The platform operates on a value-added network, or VAN-based model, with managed services.
Benefits:
Extensive retail trading partner network.
Managed services model that reduces the need for in-house EDI expertise.
Proven track record in supporting compliance with retail supply chain partners.
Possible Drawbacks:
User interface comes with a steep learning curve.
Pricing may be too high for smaller businesses.
Inconsistent customer support.
For third-party logistics providers working heavily with retail customers, SPS Commerce offers broad connectivity and reliable regulatory compliance support.
3. TrueCommerce
TrueCommerce is a well-known EDI provider that serves midsize logistics companies, fulfillment centers, and ecommerce-driven supply chains. The platform offers integrations with popular ecommerce storefronts and ERP systems, making it a practical option for 3PLs that handle a high volume of online orders.
Benefits:
Strong support for ecommerce integrations with platforms like Shopify and BigCommerce.
Library of connectors that help streamline order processing between existing business systems.
Reliable compliance support for logistics companies working with retail and ecommerce supply chain partners.
Possible Drawbacks:
Implementation can be slower compared to API-first providers.
Limited flexibility for direct WMS and TMS integrations without custom development.
Pricing can become complex as more trading partners and integrations are added.
TrueCommerce is often a good fit for 3PL companies managing common EDI transport transactions for ecommerce fulfillment operations. While it delivers solid coverage for online retail workflows, according to G2, providers may find that integrating warehouse and transportation systems requires additional customization.
It should also be noted that DiCentral, a popular EDI system long known for managed services for logistics providers, is now part of TrueCommerce.
4. Cleo Integration Cloud
Cleo Integration Cloud is an integration platform that combines traditional EDI with modern API capabilities. It is designed to support complex logistics operations by connecting 3PLs with trading partners across multiple business systems.
Benefits:
Strong support for hybrid integration that combines EDI documents with APIs.
Broad connectivity with ERP, WMS, and TMS systems to streamline logistics processes.
Visibility and monitoring tools that give logistics providers insight into data flows.
Possible Drawbacks:
Implementation can be complex and require technical expertise.
Users report the platform as having a steep learning curve.
This system offers limited advanced monitoring capabilities.
Cleo Integration Cloud is well-suited for larger 3PLs and logistics providers but may be overkill for smaller teams focused primarily on core EDI transactions.
5. Babelway
Babelway is an integration platform acquired by Tradeshift that focuses on custom mapping and automation. The system is built to give technically skilled logistics teams control over how data moves between trading partners, internal applications, and supply chain systems. Its iPaaS approach makes it appealing for providers that want flexibility in configuring data exchange.
Benefits:
Comprehensive support for EDI logistics documents like warehouse shipping advice.
Managed service model that reduces the need for in-house EDI specialists.
Strong compliance features that help logistics companies meet regulatory requirements.
Possible Drawbacks:
Steep learning curve for new users.
Possible branding confusion since being acquired by Tradeshift.
Tiered pricing that may not adequately adjust between high-volume and low-volume months.
Babelway is often chosen by 3PLs and logistics providers with strong internal IT resources that want to build customized integration flows.
6. IBM Sterling
IBM Sterling is an enterprise-class EDI system designed for global logistics organizations. Known for its depth and customization, the platform is often used by large-scale providers that need to manage several trading partners across regions.
Benefits:
Extensive support for business documents and compliance in global supply chains.
Deep integration capabilities with ERP and enterprise applications.
Scalability to handle high transaction volumes across complex logistics networks.
Possible Drawbacks:
Reports of the platform's interface not being user-friendly.
Integrations can be slow and difficult.
High licensing and implementation costs compared to other EDI providers.
IBM Sterling is best suited for multinational logistics organizations that require enterprise-grade features and can manage longer implementation timelines. For 3PLs focused on speed and agility, however, it may be more than what is needed.
Platform | Best For | Strengths | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
Orderful | Modern, API-first EDI for 3PLs | Fast onboarding, WMS/TMS/ERP integrations, flat pricing | Newer in market, less customization-heavy |
SPS Commerce | Retail-focused 3PL partnerships | Large retail network, managed services | Higher cost, inconsistent support |
TrueCommerce | Ecommerce-heavy 3PL operations | ERP/ecommerce connectors, compliance support | Slower implementation, pricing complexity |
Cleo Integration Cloud | Complex hybrid integrations | API + EDI support, visibility tools | Steep learning curve, technical expertise needed |
Babelway (Tradeshift) | Custom integration control | Flexible mapping, strong compliance | Requires IT resources, tiered pricing |
IBM Sterling | Global enterprise logistics | Scalable, compliance-heavy, enterprise integrations | Expensive, slow to implement |
Key EDI Transactions for 3PLs and Logistics
Providers rely on a range of EDI transactions in the ANSI X12 format to keep logistics processes aligned across multiple trading partners. Some of the most common include:
Warehouse shipping order (EDI 940): Instructs a warehouse or 3PL to ship goods.
Warehouse shipping advice (EDI 945): Confirms that an order has shipped, providing details such as quantities and carrier information.
Purchase order (EDI 850): Communicates product orders to a supplier or 3PL.
Advance ship notice (EDI 856): Provides shipment details to trading partners, helping them plan for inbound deliveries.
Freight invoice (EDI 210): Standardizes freight billing information for carriers and 3PLs.
Transportation carrier shipment status (EDI 214): Tracks the status of shipments, enabling real-time visibility across the supply chain.
Motor carrier load tender (EDI 204): Offers load details to carriers for acceptance or rejection, common in truckload logistics.
These transactions provide a common language for coordinating shipments, inventory, and financial records. Using an EDI platform that automates these documents can minimize delays and improve data accuracy across the entire logistics network.
Orderful: Modern EDI for 3PLs and Logistics Providers
Orderful is a cloud-native, API-first platform that integrates directly with WMS, ERP, and TMS systems. Logistics providers gain flat per-partner pricing, self-serve onboarding, and real-time data exchange without relying on costly managed services.
With faster partner connections and improved customer satisfaction, Orderful helps 3PL EDI teams focus on performance instead of manual processes or complex integrations.
FAQs About EDI Solutions for 3PLs and Logistics Providers
What is EDI for 3PL providers?
EDI for 3PL providers is the use of electronic data interchange to automate key documents like shipping orders, invoices, and shipment status updates, reducing manual work.
Which EDI transactions are most common in logistics?
Common EDI transactions in logistics include EDI 940 (warehouse shipping order), EDI 945 (warehouse shipping advice), EDI 850 (purchase order), and EDI 856 (advance ship notice).
How does EDI improve logistics operations?
EDI improves logistics by automating order processing, reducing errors, and providing real-time visibility into shipments, which improves customer satisfaction and lowers costs.
What should logistics companies look for in EDI software?
Logistics companies should look for fast onboarding, WMS/TMS/ERP integration, support for logistics-specific documents, transparent pricing, and real-time monitoring.
Is Orderful a good EDI solution for 3PLs?
Yes. Orderful provides API-first, cloud-based EDI with fast partner onboarding, real-time monitoring, flat pricing, and seamless integration with logistics systems.
Unlock Faster EDI for Logistics Operations
For 3PL providers, EDI lays the foundation for accurate data sharing, logistics automation, and stronger relationships with logistics partners. The right platform can turn electronic exchange into a growth driver instead of a cost center.
Orderful combines the ease of outsourcing with the control of an in-house system. Talk to an EDI expert today and discover how Orderful can help modernize EDI for freight, warehousing, and beyond.

